Nursing , The organization of medical care.
Nursing , The organization of medical care., The structure of the hospital. ,Admission department. Inpatient department.
Nursing-Nursing is organization of patient care.
Nursing includes three components:
- Providing a variety of patient needs. Patient needs: eating, drinking, washing, moving, help while defecation or urination.
- Creation necessary conditions for the patient stay at the hospital or at home. It means peace and quiet and also keeping beds and clothes clean.
- Alleviating the sufferings of the patient and prevention of complications.
- Nursing is a part of the patient treatment.
- It is performed by the nurse and hospital attendant (junior nurse).
The main types of nursing:
1.General nursing – is a set of measures for the care without depending on the type of disease.
2.Special nursing – is a set of measures, which depends on the specifics of the disease, its symptoms.
Care is administered in medical institutions.
PATIENT
In the center our subject – Patient.
PATIENT (A Latin word meaning to suffer or to bear) – Is a person who is waiting for or undergoing medical/nursing treatment and care.
TYPES OF MEDICAL INSTITUTIONS:
- Policlinic. Patients served by the policlinic and at home (without hospitalization), located in the city.
- Ambulatory. Patients served in the ambulatory and at home (without hospitalization), located in a small town.
- Medico sanitary department. Task – service workers of industrial enterprises, consists of a policlinic, hospital, health center, preventorium.
- Dispensary – specialized institutions in which receive treatment patients with certain pathology (tuberculosis, skin and venereal diseases, cancer etc.)
- Station of Ambulance – provides emergency specialized medical aid around the clock.
- Women’s Consultation – carry out control and treatment of women with gynecological diseases, and prenatal service.
- Hospital – carry out dynamic control and treatment of patients around the clock.
- Clinic – the hospital, which is composed of the Chair of Medical school.
- Military hospital – a hospital for sick soldiers and disabled veterans.
- Sanatorium – a hospital in the resort zone, where carry out therapy by natural and physical methods.
Hospital
The functions of the hospital:
- Diagnosis of diseases
- Treatment of diseases
- Disease prevention
The structure of the hospital:
- Admission department
- Inpatient departments
- Diagnostic department
- Pharmaceutical department
- Kitchen
- Laundry
- Administration rooms
Types of hospitalization in Hospital :
- Planned hospitalization.
The patient comes to the hospital in the direction of a doctor from the policlinic or comes to the hospital by yourself.
- Emergency hospitalization.
The patient is admitted to a hospital in an emergency (acute illness, trauma, injury and other)
- Transfer from another medical hospital.
Change the Doctor or Change the Diagnosis Center.
Admission Department

Functions of the admission department:
- Registration of patients.
- Medical examination of the patient.
- Determination department for hospitalization.
- Emergency medical aid (if necessary).
- Sanitary treatment of patients.
- Transportation of patients.
THE STRUCTURE OF ADMISSION DEPARTMENT:
1.Waiting room – a room for patients and relatives, which should be plenty of chairs, an information board.
2.Registry – special room where to registration patients.
3.Two examination rooms – for inspection therapeutic and surgical patients.
4.Sanitary room – for sanitary treatment (Sanitary and hygienic processing of patients).
5.The treatment room – to perform the injection.
6.Small Operating room (bandaging room).
7.Isolator.
8.Laboratory.
9.Room for medical staff.
10.Toilet room (WC).
11.Warehouse for the storage patient’s clothes.
Registry-Registration of Patients:
Medical documents of admission department:
1.Medical hospital card (medical history/ case history)
2.Journal of registration of patients and refusal of hospitalization.
3.Journal of examination for pediculosis.
4.Journal of registration infectious diseases.
5.Journal of telephone messages, etc.
Examination rooms. Medical examination:
- Doctor examines the patient.
- Doctor prescribes the minimum examination in accordance with the disease.
- Doctor determines the indications for hospitalization to hospital.
- Doctor provides first aid if the patient’s condition is severe (seriously ill).
- Doctor determines the volume of sanitization (sanitary treatment).
- Doctor determines the type of transportation .
Sanitary Room The structure of sanitary inspection room:
- Dressing room 1 – a room where patients undress and are inspected.
- Dressing room 2 where patients dress in clean clothes.
- Shower or bathroom, where patients take a shower or bath.
Clothes of patients is delivered in a warehouse.
If the patient revealed an infection, his clothes is delivered in the disinfection chamber. The patient is placed in isolator or hospitalized to the infectious diseases hospital.
Sanitary treatment
(Sanitary and hygienic processing of patients):
Types of sanitary treatment :
- Complete processing
- Partial processing
Algorithm Сomplete sanitary treatment :
- Examination of the hair and skin (detection pediculosis);
- Gooming of nails and hair (if needed);
- Shaving (if needed);
- Take a shower or hygienic bath.
Algorithm Partial sanitary treatment :
- Examination of the hair and skin (detection pediculosis);
- Partial wash and wiping the skin.
Partial processing is performed if the patient in critical condition.
Inspection of skin and hair of the patient
- Examination of the skin and hair of the patient is carried out to detect lice.
- Pediculosis – the lesions of skin and hair as a result of parasitism on the body lice.
- Pediculosis – a specific parasitism of lice on human, which feed on its blood.
- Lice – are vectors of typhus and relapsing fever and other rickettsial diseases.
Lice exist on our planet for about 40-50 million years.
The history of mankind has “only” about 2.5 million years.
There are about 250 species of lice.
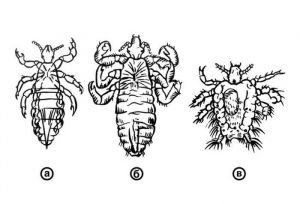
On the body of human parasites three types of lice.
Types of lice
- The head lice – louse affects the scalp;
- Body (clothes) louse – is usually a parasite on the human clothes. However, she lives and lays eggs (nits) in clothing and feeds on temporarily moving from clothing on the skin.
- Pubic lice – striking surface hairy pubic area, hairy underarms, and face – mustache, beard, eyebrows, eyelashes.
- a) Head lice; B) Body (clouthes) lice C) Pubic lice
Signs of Pediculosis:
- Presence of adult insects,
- Their eggs (nits),
- Skin itch,
- Traces of scratching on the skin
Details
- Pediculosis is associated with poor hygiene, crowded living conditions and exposure to other individuals with pediculosis.
- Lice can be transferred from person to person through direct contact. It gets easily transmitted from person to person perhaps sleeping together, sitting together etc. They can also be transmitted through clothing, bedding,combs etc.
- The itching of the scalp is a source of discomfort to the client causing restlessness and insomnia.
- The lice are blood suckers and cause anaemia.
- They spread the disease e.g. typhus fever, relapsing fever,trench fever.
- Itching of the scalp results in the scalp injury and the injured area is subjected to infection which lead to infected glands.
Prevention of Pediculosis
Prevention is easier than controlling. For this, proper personal hygiene concept should be practiced by everybody in their lives.
- Do not wear other people’s hats, Do not use the comb of strangers.
- Combing the hair daily, washing it frequently, keeping the skin and clothing clean will solve the problem.
- Any client complaining of itching or if scratches the head,needs thorough examination of the hair and scalp,body and linen to discover lice.
- If lice are found on the client’s head or body,follow the prescribed treatment.
Algorithm of actions:
- Wash hands. Wear protective clothes (gown mask and cap). Reason – The gown and cap protect the nurse from the infestation with lice.
- Spread out oilcloth, seat the patient on a chair or couch.
- Part the hair into small sections and apply the parasiticide on the hair and scalp, rubbing gently. In long hair, the medicine is to be applied along the whole length of the hair.Reason – Thorough application of the parasiticide ensure thorough destruction of the lice.
- Roll up the long hair to the top of the head and cover the had with the cap or triangular bandage or by a towel folded diagonally. Secure it with pins. Sustain the necessary time, according to methodical instructions on the medication. Reason – Covering the head with the towel prevents the spread of the lice to other areas of the body.
- Wash off medication with warm water and with shampoo.
- Rinse hair with warm water and 6% vinegar.
- Carefully comb out lice and nits louse with comb.
- Disinfect object of care and protective clothes.
- Make an entry in the patient’s medical document. Marking «P» on the title page of Medical hospital card (medical history).
- 10 . Process the room.
N.B. After 7 days to see the patient again. If necessary, repeat the procedure.
Parasiticides Used in the treatment of pediculosis
- Nitttifor
- Pedilin
- Couple plus
- Paranit
The instruction to the drug Nittifor
- Method of application and dose:
Hair is liberally moistened with a solution with a cotton swab, rubbing the drug into the hair roots. Consumption per person – 10 to 60 ml, depending on the density and length of hair. After the treatment the head is covered with scarf, and after 40 min drug wash off with warm running water with soap or shampoo. After washing a hair comb to remove dead insects. If live lice are found 7 days after treatment is recommended to repeat the treatment. - In the case of existing danger of re-infection in a group (school, kindergarten) medicine to apply after shampooing and leave it on the hair after drying. Applied to the hair, the drug retains its activity for approximately 2 weeks (does not allow to reproduce again caught hair lice). To repeat the treatment after every hair wash. The dead nits are removed from hair with a thick comb or one, because they are firmly attached to the hair.Solution. A bottle containing 24 ml of the drug, calculated on a three-day course of treatment. For ease of use on the bottle marks.
Applied externally in the form of freshly prepared 0.4% aqueous emulsion, for which 1/3 of the contents of the vial (8 ml) is added to 100 ml of boiled water at room temperature. The finished emulsion 1 time a day (at night) thoroughly rubbed into the skin of the upper extremities, torso, and then lower extremities.
Not be processed skin of the face and neck, and scalp. At the end of the treatment on the fourth day the patient should take a shower and to hold a change of underwear and bed linen.
Patient’s transport
Method of transportation of the patient in the hospital:
- On a stretcher (gurney)
- A wheelchair
- On foot (accompanied by medical personnel – nurse!)
REMEMBER
- The doctor conducting the examination, determines the method of transportation of the patient.
- Necessary take into account the patient’s condition.
- Seriously sick (can not move) are transported to the office on a stretcher or in a wheel chair. Means of transport (wheelchairs, stretchers) are provided with sheets and blankets that must be replaced after each patient.
- Patients that move independently from admissions go to the house accompanied by nurses.
Means of transport:
- Wheelchairs
- Gurney
- Stretchers

Algorithm. Transportation a patient on a stretcher (gurney)
1.Wear gloves.
2.Cover the stretcher with bedsheet.
3.Shifting the patient from bed to stretcher:
Put the head end of the stretcher perpendicular to the foot end of the bed (medical couch) (figure 1). If the area the house is small, put the stretcher parallel to the bed (figure b).
If three medical personnel: first nurse put hands under the head and shoulder of the patient, second – the pelvis and the upper part of the hips, third – under the middle of the thighs and shins.
If two medical personnel: first nurse put hands under the neck and shoulder of the patient, second – under the lower back and knees.
- Raise the patient, turn in the direction of stretcher on 90 ° (perpendicular shifting) or on 180 ° (parallel shifting).
- Place the patient on a stretcher, cover him.
- Carry the stretcher (roll the gurney) in the department by head forward to evaluate possible changes patient’s condition.
- In the ward put the head end of the stretcher to the foot end of the bed.
- Shifting the patient from stretcher to bed (rules above).
- Process the stretcher.
- Put gloves in disinfectant.
- Wash hands.
Transportation on a stretcher
- Carry a patient on a stretcher should be without haste and shaking. Carry the patient down the stairs feet forward. Carry the patient Up the stairs, the head forward.
Shifting the patient from bed to wheelchairs

INPATIENT DEPARTMENT
(therapeutic or surgical department)
The staff of the Inpatient department:
- Head of Department
- Doctors (clinical intern)
- Senior nurse
- Ward nurse
- Treatment nurse (procedural nurse)
- Junior nurse
- Dressing nurse (surgical Department)
Types of Nurse and Function
SENIOR NURSE – the most experience nurse of department.
Functions:
- Organize the work of Ward and Junior nurses;
- Supply the drug, medical equipment, medical instruments in Inpatient department for nursing care
- Strict accounting of narcotic and toxic drugs.
WARD NURSE
Functions:
- Admission patients.
- Carry out of nursing examination (weight, height, thermometry, blood pressure, pulse).
- Organization General nursing. The provision of hospital regimes, personal hygiene, motor activity, nutrition, pharmacotherapy.
- Organization Special nursing (depends on the disease).
TREATMENT NURSE
Functions:
- Perform doctor’s appointments (parenteral methods of administration – subcutaneous, intramuscular, intravenous injections, intravenous infusion)
- Helps the doctor during manipulation (for example, determination of blood group).
- Take of a blood from a vein for biochemical research
JUNIOR NURSE
Functions:
- Regular wet cleaning of Inpatient department .
- Sanitary and hygenic processing of the patients.
- Transportation of patients.
- Implementation nursing for the seriously ill (Help to Ward nurse).
- Disinfection of used subjects of care for patient.
- Сollecting and disposing of medical waste.
The Structure of the Inpatient Department:
1.Nursing station (office)
2.Wards for patients.
3.Treatment room.
4.Manipulational room – Cabinet for medical procedures (such as enema, sensing and other manipulation).
5.Rooms for medical staff.
6.Dining room.
7.Shower room.
8.WC (toilet room).
9.Dressing room (surgical Department)
Also Read this Article
Infectious safety Nosocomial infections Prevention of nosocomial infections
Nursing station. Organization the work of nursing station
Nursing station (office) – It is workplace of Ward nurse, located in the hall.
Equipment nursing station
- 1.Table
- Chairs (2 – 3)
- Telephone.
- Capboard for medicines.
- Table lamp
- Clock.
- Refrigerator for foodstuff.
- Signalization.
- Device to measure blood pressure
- Medical scales
- Height meter
Admission patients is a process of receiving a new patient to an individual unit (ward) of the hospital.
Admission patients includes:
1.Check for orders of admission.
2.Assess the patient’s immediate need and take action to meet them. These needs can be physical (e.g. acute pain) or emotional distress, (upset).
3.Make introduction and orient the patient.
4.Perform baseline assessment of patients:
- Consciousness
- Temperature
- Respiration
- Pulse
- blood pressure.
- Measure the weight of the patient
- Waist size
- Height is measured (if required)
- Documentation
An algorithm for the measurement of body weight
Equipment.
- Medical electronic scales
- Oilcloth (or disposabl napkin)
- Gloves
- Medical documentation (temperature sheet)
- Сontainer for disinfection
Algorithm:
- Explain to the patient the purpose and procedure course. Obtain patient’s consent.
- Conduct hygienic washing hand and processing hand. Put the gloveson.
- Put on the surface of scales the oilcloth (or disposable napkin).
- The patient must remove their shoes.
- The patient must carefully stand on the center platform on the oilcloth.
- Remember result.
- Ask the patient get off on the floor carefully.
- Offer the patient put on shoes and walk to the ward.
- Conduct disinfection used material (or utilization napkin).
- Take the gloves off and put them in the container for disinfection.
- Wash hands hygienic way.
- Make a record of results in a medical documentation.
Algorithm measurement the growth of the patient
Equipment.
- Medical stadiometer
- Oilcloth (or disposabl napkin)
- Gloves
- Medical documentation (temperature sheet)
- Сontainer for disinfection
Algorithm:
- Explain to the patient the purpose and procedure course. Obtain patient’s consent.
- Conduct hygienic washing hand and processing hand. Put the gloves on.
- You must cover the platform of the stadiometer with an oilcloth (or disposable napkin). The patient must remove their shoes and cap.
- Ask the patient to stand on a platform of stadiometer, covered with oilcloth.
- Explain what patient must straighten your back during the measurement of growth, to touch vertical strips by four points: neck, shoulders, buttocks and heels.
- Check the position of the patient’s head. The line connecting the external corner of the eye and upper edge of ear must be horizontal.
- Lower the measuring bar on the top of the patient head. To fix the bar with hand.
- Ask the patient get off on the floor.
- Offer the patient put on shoes and walk to the ward.
- Conduct disinfection used material (or utilization napkin).
- Take the gloves off and put them in the container for disinfection.
- Wash hands hygienic way.
- Make a record of results in a medical documentation .
Anthropometry
- Anthropometry – evaluation of human body by measuring height and body weight.
- Today in clinical practice is widely used calculation of body mass index (BMI) which is calculated by the formula:
BMI=body weight (kg) / height2 (m).
- The ideal BMI is 24.
- In this BMI, the mortality rate of man minimum. A BMI of over 30 means obesity, less than 18 – underweight.
The waist size
- In normal waist circumference (FROM) women should not exceed 80 cm, and for men 94 cm.
- If the circumference of your waist is higher than normal, then you are at risk of cardiovascular diseases and type II diabetes.
«The bigger the waistline the shorter the life!»
Patient Care Unit
Patient Care Unit: is the space where the patient is accommodated in hospital or patient home where to receive care.
The patient unit in the hospital is of three types:
1.Private room – is a room in which only one patient be admitted
2.Semi private room – is a patient unit which can accommodate two patients
3.Ward – is a room, which can receive three or more patients.
Patient Care Unit сonsists of a hospital bed, bed side stand, chair, overhead light, waste container and others as needed and available.
Hospital Bed. Gatch bed: a manual bed which requires the use of hand racks or foot pedals to manipulate the bed into desired positions i.e. to elevate the head or the foot of the bed.
Types of Hospital Regime:
1.Therapeutic protective regime
2.Individual (motor ) regime
3.Hygienic regime
4.Sanitary and epidemiological regime.
2.Individual motor regime – the amount of patient`s physical activity.
Types:
- Strict bed rest regime
- Bed rest regime
- Ward regime
- Free regime
Strict bed regime – A patient must not move yourself and change position in bed.
For example: The strict bed regime
is prescribed by the doctor during the first hours after surgery, myocardial infarction, and others.
Bed rest regime – The patient may move only in bed.
This regime is prescribed in order to increase motion activity while recovery.
Ward regime – The patient may sit, stand, walk carefully in hospital ward.
Free regime –The patient may move freely within a ward or department.
3. Hygienic regime – a system of requirements for hygienic conditions at the hospital.
For example:
- Walls in the wards must be painted with oil-based paint. No wallpaper on the walls. Such walls are difficult to wash.
- Beds must be made of metal, because beds made of wood can absorb blood, urine and so on.
- Walls in the medical treatment room must be tiled.
Medical privacy
All information received by a medical worker about the patient – is a medical privacy.
Medical privacy includes:
- information about the treatment in the hospital;
- information about a person`s health status;
- information about the diagnosis;
- other information received during the examination and treatment.
A doctor in Russia can violate the medical secrecy in the following situations:
1) If a patient has mental disorders, therefore, they can not express their will;
2) if there is the threat of infectious disease dissemination or poisoning;
3) if there is a criminal investigation;
4) If the patient is a child;
5) If the disease is a result of violent act.
For example, a knife wound.
Iatrogenic illnesses
An incompetent medical worker may do harm to the patient.
The consequences of the medical negative action are called “Iatrogenic illnesses”.
Types of iatrogenic illnesses:
- Psychogenic iatrogeny
- Medicamental iatrogeny
- Manipulation iatrogeny
- Silent iatrogeny
- Psychogenic iatrogeny – the pathology, caused by careless words and actions of the doctor.
- Medicamental iatrogeny – is a result of drug effect.
- Manipulation iatrogeny – is a complication, appeared during medical procedures.
- Silent iatrogeny – a result of inaction of a medical worker.
Download ppt Nursing , The organization of medical care., The structure of the hospital. ,Admission department. Inpatient department.



