Care for Elderly and old People, Seriously ill
Care for Elderly and old People, Seriously ill
Care for Elderly and old People:
Modern age standards were adopted by the European regional Office of WHO (World Health organization) in 1963:
- Elderly Age – 60-74
- Gerontal (Senil) Age – 75-89
- Long-livers – 90 and older
The features of elderly and senile age
- Involutional functional and morphological changes in the various organs and systems. Back development and aging come with age.
- Several diseases.
- Mostly chronic diseases.
- Atypical clinical course of the disease.
- The presence of «senile diseases» (osteoporosis, benign prostatic hyperplasia, prostate cancer, Alzheimer’s disease and others).
- Disorder protective, immune responses.
- Disorder of the social and psychological status. The main causes of social disadaptation. Anxiety, depression, hypochondriac syndrome often develop against this background.
Principles for the Nursing Care of elderly Patient:
- Injury prevention
- Control pharmacotherapy
- Diet nutrition
- Prevention of chronic constipation
- Prevention of colds
- Control of physical inactivity
- Prevention of insomnia
- Providing personal hygiene of the patient
INJURY PREVENTION
Bruise and fracture bones are the most common injury in the elderly patient.
Bruise and fracture bones (especially fracture of neck of femur) violate movement of patients, inevitably lead to complications, such as pneumonia, pulmonary thromboembolism, lead to death.
Injury prevention:
1.Use of aids for movement if patients has movement violation( cane, auxiliary means for movement- support for hands, wheelchair).
2.Do not clutter the room with furniture.
3.Illumination in the night time should have in the corridors and wards.
4.Floor must be dry (puddles wiped immediately).
5.Assistance to patients at the bathroom. A nurse is present and helps while bathing; to maintain the patient while getting in and out of bath.
CONTROL PHARMACOTHERAPY
- Dosage of medication
- Frequency of intake drugs
- Regular intake of medicinal preparation
- Features pharmacokinetics (some drugs are taken before a meal, the other drugs after eating)
- Optimal combination drugs with food, the other drugs
The Nurse Should Monitor these Moments.
Diet Nutrition
Characteristic of Diet for Elderly Patient:
- Low content of calories
- Reduced fat
- A small volume of food
- Nutrition should be divided (4 – 5 times a day),
- High content of fruit and vegetables.
PREVENTION OF CHRONIC CONSTIPATION
The nurse should provide (monitor):
- Regulation of defecation by diet
- Regular intake of purgative preparation
- Cleansing enema or oily enema (for chronic constipation)
PREVENTION OF COLDS
Duties of a nurse:
- The ward should be empty during the ventilation.
- Patients should be dressed in accordance with the temperature of environment.
- Infectious patients should be isolated.
Elderly and old people are more sensitive to cold drafts.
CONTROL OF PHYSICAL INACTIVITY
- Medical gymnastics if there are no contraindications
- Keep the individual motor mode
PREVENTION OF INSOMNIA
- Walk before bedtime
- Limit fluid intake before bedtime
- Empty the bladder before going to sleep
- A warm shower before bedtime
- Intake of hypnotics if necessary
Also Read this Article
PROVIDING PERSONAL HYGIENE OF THE PATIENT
Patients who need help the nurses to provide personal care:
- Seriously ill clients.
- Paralysed clients.
- Unconscious patient.
- Malnourished patients.
The nurse performs:
- Eyes care (daily),
- Ears care (daily),
- Nose care (daily),
- Care of the oral cavity (daily),
- Hair care (1 time per seven days),
- Skin care (1 time per seven days),
- Care of the perineum (daily and after each defecation)
Types of the Patient Positions (in the bed)
The main place of staying of the patient in a hospital is bed.
Depending on the patient’s condition and doctor’s prescriptions the following
Types of the Patient Positions can be :
Three Types
- Active position – the patient can move freely and easily.
- Passive position – in the case of impossibility of active movements of patients (in a state of unconsciousness, severe weakness).
- Forced position – the patient is taken to reduce the severity of symptoms.
Example of Forced Position.
- Disease – bronchial asthma. The main manifestation – dyspnea and asphyxia.
- Forced Position. Patient sits, leans with hands. In the result the auxiliary respiratory muscles are involved in the process of breathing. Severity of dyspnea is reduced.
Example of Forced position
- Disease – Abdominal Pain.
- Forced position. «The fetal position» – patient lies on his side, hands and feet pressed against the abdomen. In the result the pressure is decreasing in the stomach. Severity of pain is reduced.
PERSONAL HYGIENE
Oral Hygiene
- Oral hygiene means brushing the client’s teeth or cleaning the dentures according to the integrity of the client’s teeth, gums, mucus membrane and lips. Oral cavity is an ideal place for bacterial growth by providing warms, moisture, food supply from the residual foods on and between the teeth and a protected environment. The number of bacteria in the mouth depends upon the degree of cleanliness of the mouth. A neglected mouth can cause various types of infection in the oral cavity.
- Infection of the mouth can spread to neighboring structures leading to the following: parotitis, sinusitis, otitis media, adenitis, tonsillitis)
Systemic infections
The streptococci which is a normal inhabitant of the oral cavity enter into pulp cavity of the teeth. Pus is formed in the pulp cavity which becomes a focus of infection and spread to the distant parts of the body via blood stream causing various systemic diseases such as following: Rheumatic arthritis, Bacterial endocarditis, Nephritis, Gastritis, Anorexia)
Prevention of Complications
1.A clean mouth makes a person feel clean and comfortable. The mouth should be rinsed after every meal to dislodge any food particle left between the teeth.
2.All persons who are unable to attend the mouth should be assisted to clean the mouth. The following client’s should have mouth care. They may be given mouth care every 2 hours or 4 hours:
- Seriously ill clients.
- Paralysed clients.
- Unconscious patient.
- Patients breathing through the mouth.
- Malnourished and dehydrated patients.
- Patients who are not taking oral feed.
3.Prevent dehydration of the tissues by the administration of enough fluids.
Also Read this Article
Infectious safety Nosocomial infections Prevention of nosocomial infections
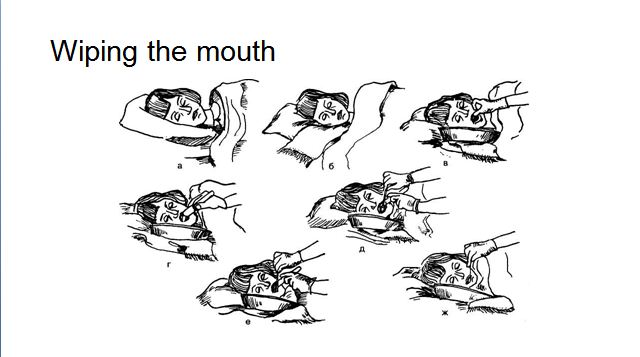
WIPING THE MOUTH
Wiping of the mouth is conducted to a seriously ill patient or unconscious.
Purpose: Oral Hygiene, Prevention of inflammatory Processes in the oral cavity.
Equipment. Sterile: gauze napkin, medical tray, spatula, dressing forceps, antiseptic solution in measuring glass (0,02% aqueous solution furacin or 0,9% physiological solution of sodium chloride), petrolatum. Towel, gloves, a container for disinfection (tray).
Algorithm:
1.Explain to the patient the purpose and procedure course. Obtain patient’s consent.
2.Conduct hygienic washing hand and processing hand. Put the gloves on.
3.Put the towel around the patient’s neck.
4.Lay down the patient in the supine position, raise the head end of the bed at an angle 45° (Fowler‘s position). Turn the head to one side.
5.Take gauze napkin by forceps, moisten with an antiseptic solution.
6.Pull the corner of mouth with a spatula.
7.Process the teeth on the internal side, starting with molars (left and right).
8.Change the gauze napkin.
9.Process the teeth with external side, starting with molars (left and right).
10.Turn the head in other side. Perform manipulation on the other side, changing the gauze napkins.
11.Remove surplus liquid around the mouth by dry gauze napkins.
12.Ask the patient to stick his tongue.
13.Remove fur on tongue (wiping from the root of the tongue to the tip by gauze napkin, moistened in an antiseptic solution.
14.Smear skin with vaseline, if need.
15.Conduct disinfection used material.
16.Take the gloves off and put them in the container for disinfection.
17.Wash hands hygienic way.
18.Make a record of results in a medical documentation.
Remember!
- If the patient has plaque on his tongue and lips, first, these places should be smear oil. After a short interval of time gently remove plaque.
19.Oral mucosa of critically ill patients is characterized by dryness. It is recommended to lubricate the oral mucosa by oil (vaseline, olive, peach, sea buckthorn).
20.Dentures must be removed before bedtime and processed. Store in a clean container.
Wiping the Mouth
IRRIGATION ORAL CAVITY
- Irrigation oral is conducted in the presence in inflammatory changes of the oral mucosa.
- Irrigation oral is carried out with antiseptic solutions or drugs.
Purpose: Medical.
Equipment. Sterile: gauze napkin, tray, spatula, forceps, syringe of Janet, antiseptic solution in measuring glass (0.02% aqueous solution furacin or 0.9% physiological solution of sodium chloride, the infusion of calendula and chamomile), vaseline, warm boiled water. Unsterile: towel, gloves, a container for disinfection (tray).
Algorithm:
- Explain to the patient the purpose and procedure course. Obtain patient’s consent.
- Seat the the patient or lay down his in the Fowler‘s position.
- Conduct hygienic washing hand and processing hand. Put the gloves on.
- To cover neck and chest with a towel.
- Attach the tray to the chin.
- Ask the patient to close up his teeth. Turn the head to one side.
- Fill up into the syringe of Janet solution for irrigation.
- Pull the corner of his mouth with a spatula. Enter the сannula of the syringe into the space between the cheek and teeth.
- Enter the tip of the syringe Janet in the space between the cheek and teeth.
- The space between the cheek and teeth wash out with an antiseptic solution.
- Rinse the mouth with warm boiled water.
- Turn the head in other side. Perform manipulation on the other hand.
- Remove surplus liquid from by dry gauze napkin.
- Conduct disinfection used material.
- Take the gloves off and put them in the container for disinfection.
- Wash hands hygienic way.
- Make a record of results in a medical documentation.
Remember!
- Remove dentures before performing this procedure.
- Oral irrigation is strictly prohibited carry out by patient in unconsciousness. Liquid can get into the respiratory tract, may develop asphyxia.
- Wiping of the mouth should always be preceded the irrigation oral.
Сare of Eyes
- A common problem of the eyes are secretions that dry on the lashes as crusts. This may need to be softened and wiped away under sterile conditions. Eyes are cleaned from the outer to the inner canthus. When sterile procedure is required, each eye is cleaned with separate swabs, swabbing each eye once only. This prevent spread of infection from one eye to other and to avoid possible recontamination of the same eye.
WIPING THE EYE
- Purpose: Prevention of inflammatory Eye diseases.
- Equipment. Sterile: tray, gauze napkins, tweezers, antiseptic solution in measuring glass (0.02% aqueous solution furacin). Unsterile: gloves, a container for disinfection (tray).
Algorithm:
- Explain to the patient the purpose and procedure course. Obtain patient’s consent.
- Conduct hygienic washing hand and processing hand.
- Put the gloves on.
- Inspect the eyes, assess the condition.
- Take a gauze napkin with tweezers, moisten in an antiseptic solution, take the gauze napkin in your right hand.
- Wipe eyelid in the direction from external corner of the eye to the internal. Use several gauze napkins, if necessary.
- Then wipe eyelid with a dry gauze napkin in the same direction.
- Similarly treat the other eye.
- Conduct disinfection used material.
- Take the gloves off and put them in the container for disinfection.
- Wash hands in hygienic way .
- Make a record of results in a medical documentation.
LAYING OPHTHALMIC OINTMENT TO THE LOWER EYELID FROM THE TUBE
- Purpose: Medical.
- Equipment. Sterile: Gauze Napkins, tray tube of ointment. Gloves, tray, container for disinfection (tray).
Algorithm:
- Explain to the patient the purpose and procedure course. Obtain patient’s consent.
- Conduct hygienic washing hand and processing hand. Put the gloves on.
- Seat the patient face to light. Gently tilt the head back or lay patient on his back without a pillow. Offer the patient to look up.
- Take the gauze napkin in the left hand. Attach the gauze napkin to the inferior eyelid . Pull the lower eyelid down.
- Use your right hand to squeeze the ointment from the tube on the conjunctiva of the lower eyelid. From the internal to the external corner of the eye.
- Release the lower eyelid and ointment is pressed against the eyeball.
- Put in the other eye ointment. Use a new gauze napkin .
- Conduct disinfection used material.
- Take the gloves off and put them in the container for disinfection.
- Wash hands hygienic way.
- Make a record of results in a medical documentation.
Care of Nose and Ears
- The nose and ears require minimal care in the daily life. Excessive accumulation of secretions make the client sniff or blow the nose. The secretions can become crusted and obstruct the airway (another nares).
- For patients who cannot remove the secretions, assistance is necessary to clear the congestion and protect the nasal mucosa. External crusted secretions can be removed with a wet wash cloth or a cotton applicator moistened with oil, normal saline or water.
- When there is poor hygiene of the ears, debris may accumulate behind the ear and the anterior aspect of the external ear. This can lead to ulceration of the skin. A common problem of the ears is the collection of cerumen or ear wax in the external auditory canal. This may cause a person some difficulty in hearing.
- It can cause discomfort when it hardens. Many people remove wax from their ears by using sharp objects which can traumatize the ear drum. Warm liquid or a vegetable oil instilled into the ear can soften the wax and it can be easily removed.
EAR CARE
- Purpose: Warning hearing loss due to the accumulation of sulfur.
- Equipment. Sterile: tray, cotton turundas, 3% hydrogen peroxide solution in measuring glass , antiseptic solution in measuring glass, gauze napkin. Gloves, tray, container for disinfection (tray).
Algorithm:
- Explain to the patient the purpose and procedure course. Obtain patient’s consent.
- Conduct hygienic washing hand and processing hand. Put the gloves on.
- Turn the head to one side.
- Use tweezers to moisten the gauze in an antiseptic solution.
- Wipe the outside of the ear. Wipe the inside of the ear.
- Using tweezers, moisten a cotton turunda with 3% solution of hydrogen peroxide.
- Put the turunda in the right hand.
- With the left hand pull the ear of the patient to the side and up. For straightening of the auditory canal.
- Enter the turunda with rotational movements in the external auditory canal to a depth of 1 cm.
- Leave cotton turunda in the ear canal for 2-3 minutes.
- Remove the turunda with rotational movements in the same direction.
- Turn the head in other side. Perform manipulation on the other side.
- Conduct disinfection used material.
- Take the gloves off and put them in the container for disinfection.
- Wash hands hygienic way.
- Make a record of results in a medical documentation.
Also Read this Article
Dripping the Drops in Ears
- Purpose: Preventive, Curative.
- Equipment. Sterile: pipette, cotton turundas, tray, warm ear drops. Gloves, container for disinfection (tray).
Algorithm:
- Explain to the patient the purpose and procedure course. Obtain patient’s consent.
- Conduct hygienic washing hand and processing hand. Put the gloves on.
- Seat the patient or lay down. Turn the head to the opposite side (tilt the head if the patient sits).
- Take the pipette in your right hand. Put the medicament in the pipette.
- With the left hand pull the ear of the patient to the side and up. Instillation ear drops (3-5 drops).
- Leave the patient in this position as long as necessary to get the needed effect (from 1 to 15 minutes).
- Turn the head in other side. Perform manipulation on the other side.
- Conduct disinfection used material.
- Take the gloves off and put them in the container for disinfection.
- Wash hands hygienic way.
- Make a record of results in a medical documentation.
Remember
- The ear canal should be cleaned before installation of the drops.
- The drug needs to be heated in a water bath to 37 ̊ C before instillation.
LAYING THE OINTMENT TO THE EAR
- Purpose: Medical.
- Equipment. Sterile: cotton turundas, ointment, tray. Gloves, container for disinfection (tray).
Algorithm:
- Explain to the patient the purpose and procedure course. Obtain patient’s consent.
- Conduct hygienic washing hand and processing hand. Put the gloves on.
- Seat the patient or lay down. Turn the head to the opposite side (tilt the head if the patient sits).
- Apply the ointment a sterile cotton turunda.
- With the left hand pull the ear of the patient to the side and up.
- Enter the turunda with rotational movements in the external auditory canal.
- Turn the head in other side. Perform manipulation on the other side.
- Conduct disinfection used material.
- Take the gloves off and put them in the container for disinfection.
- Wash hands hygienic way.
- Make a record of results in a medical documentation.
Remember!
- The ear canal should be cleaned before introduction of ointment in the ear.
Treatment of the Nasal Passages
Objective: To prevent violation of nasal breathing.
Equipment. Sterile: pipette, cotton turundas, tray, oil (vaseline, sea buckthorn and more). Gloves, container for disinfection (tray).
Algorithm:
- Explain to the patient the purpose and procedure course. Obtain patient’s consent.
- Conduct hygienic washing hand and processing hand. Put the gloves on.
- Seat the patient or lay down. Gently tilt the head back.
- Take the cotton turunda with tweezers. Moisten a cotton turunda in vaseline oil. Put on the turunda in the right hand.
- Enter the cotton turunda into the nasal passage. Leave in for 2-3 minutes.
- Remove turunda with rotational movements in the same direction.
- Remove the turunda together with softened crusts (with rotational movements in the same direction).
- Conduct disinfection used material.
- Take the gloves off and put them in the container for disinfection.
- Wash hands hygienic way.
- Make a record of results in a medical documentation.
Dripping the Drops in Nose
Purpose: Medical.
Equipment . Sterile: cotton balls, tray, pipette (or individual bottle), drug. Non-sterile: gloves, container for disinfection (tray).
Algorithm:
- Explain to the patient the purpose and procedure course. Obtain patient’s consent.
- Conduct hygienic washing hand and processing hand. Put the gloves on.
- Seat the patient or lay down. Gently tilt the head to the side instillation.
- Take the cotton balls in the left hand. Press them to the palm of the little finger.
- Put the pipette in your right hand. Put the medicament in the pipette.
- Raise the tip of the nose with your left thumb.
- Enter the pipette in the nasal passage to a depth of 1-1.5 cm, without touching the walls.
- Drip 4-5 drops in the nasal passage.
- Compress the wing of nostril with a cotton ball.
- Turn the head in other side. Perform manipulation on the other side.
- Conduct disinfection used material.
- Take the gloves off and put them in the container for disinfection.
- Wash hands hygienic way.
- Make a record of results in a medical documentation.
THEORETICAL QUESTION
- Modern age standards were adopted by the European regional Office of WHO (World Health organization) in 1963.
- The features of elderly and senile.
- Principles for the nursing care of elderly patient.
- Injury prevention.
- Control pharmacotherapy.
- Diet nutrition.
- Prevention of chronic constipation.
- Prevention of colds.
- Control of physical inactivity.
- Prevention of insomnia.
- Types of the patient positions.
PRACTICAL SKILLS
- Wiping the mouth
- Eyes care
- Ears care
- Nose care
- Dripping the drops in nose
- Dripping the drops in Ears
- Dripping the drops in Eyes
Download PPT Care for Elderly and old People, Seriously ill



